BAMBOO INTRODUCTION
Bamboo is a type of grass from the Poaceae family, known as one of the fastest-growing plants on the planet. The unique feature of bamboo is its formation of long, hollow internodes.
With over 1,000 different species, bamboo can be found in various regions around the world, from tropical to temperate zones. Bamboo not only plays a crucial role in ecosystems but also holds significant economic and cultural value for many communities.
GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS AND STAGES OF BAMBOO
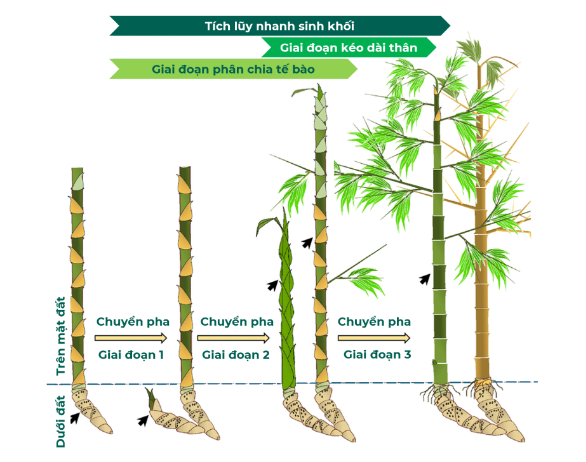
Bamboo is notable for its rapid growth and adaptability to different environmental conditions. The growth process of bamboo is divided into three main stages:
1. Shoot Stage:
- During this stage, new bamboo shoots begin to emerge from the base. Under ideal conditions, bamboo shoots can grow up to 91 cm per day.
- Bamboo roots develop robustly, allowing the plant to absorb sufficient water and nutrients from the soil.
2. Growth Stage:
- After approximately 3-4 years, bamboo reaches maturity. At this stage, the bamboo has attained larger height and diameter, and the bark becomes tougher.
- During this stage, the plant continues to grow, but at a slower rate.
3. Stabilization and Aging Stage:
- After about 7-10 years, bamboo begins to enter the aging stage. During this period, the bamboo starts to release CO2 back into the environment, its growth slows down, and the plant eventually dies to make way for new shoots.
- The lifecycle of bamboo ends, but new growth begins from the base of the plant.
BAMBOO CHARACTERISTICS AND SUSTAINABILITY VALUE
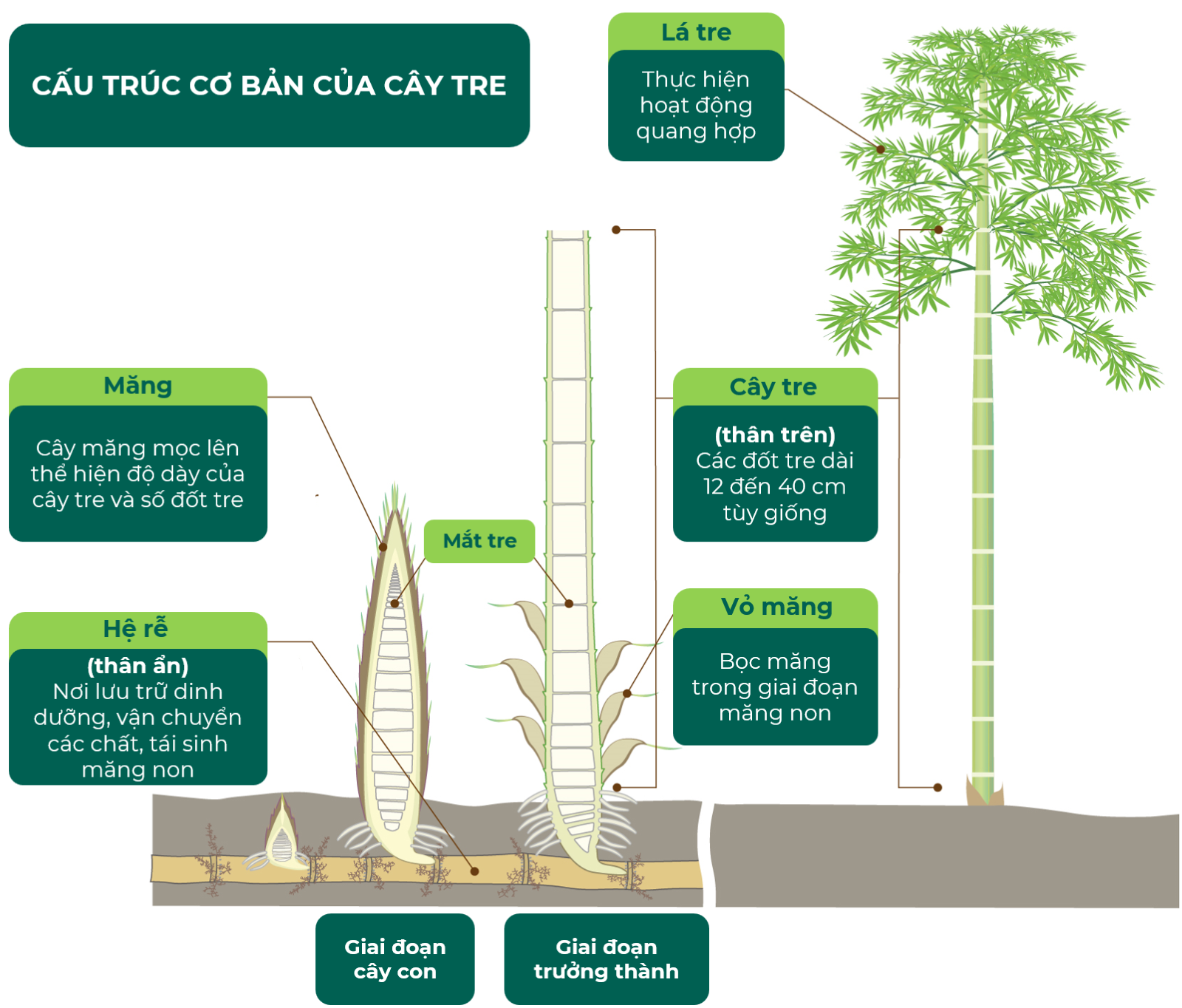
The roots, stems, branches, leaves, shoots, sheaths, and other parts of bamboo can be fully utilized. Bamboo stems have the widest range of applications due to their superior properties, such as high durability, good flexibility, and stable performance, making them suitable for building materials, furniture, weaving, crafts, paper, daily necessities, and more. Today, bamboo is recognized as a green and sustainable material due to its short growth cycle, rapid growth rate, wide distribution, and abundant yield.
1. Sustainability
- Bamboo can naturally regenerate from its base and does not require replanting after harvest. This helps minimize deforestation and maintain ecological balance.
- Bamboo absorbs significantly more CO2 than other types of plants, helping to reduce greenhouse effects and climate change.
2. Versatility
- Bamboo can be used in various industries such as construction, furniture, paper, and even food. Bamboo products often have high durability and are environmentally friendly.
- Bamboo is a key material in many traditional crafts, contributing to cultural preservation and creating job opportunities for local communities.
3. Economic Value
- Growing and processing bamboo is less costly compared to many other types of plants, providing high returns for farmers and businesses.
- Bamboo products are increasingly popular in international markets, creating export opportunities and boosting local economies.
